patch机制
数据更新视图
当对 model(数据模型) 进行操作的时候,会触发对应 Dep 中的 Watcher 对象。Watcher 对象会调用对应的 update 来修改视图。最终是将新产生的 VNode 节点与老 VNode 进行一个 patch 的过程,比对得出「差异」,最终将这些「差异」更新到视图上。
跨平台
因为使用了 Virtual DOM 的原因,Vue.js具有了跨平台的能力,但是 Virtual DOM 终归只是一些 JavaScript 对象,要想调用不同平台的API,需要依赖一层适配层,将不同的API封装在内,以同样的接口对外提供。
例如:
const nodeOps = {
setTextContent (text) {
if (platform === 'weex') {
node.parentNode.setAttr('value', text);
} else if (platform === 'web') {
node.textContent = text;
}
},
parentNode () {
//......
},
removeChild () {
//......
},
nextSibling () {
//......
},
insertBefore () {
//......
}
}API
一些在 patch 过程中会用到的API,他们最终都会调用nodeOps中的相应函数来操作平台
insert
insert 用来在 parent 这个父节点下插入一个子节点,如果指定了 ref 则插入到 ref 这个子节点前面。
function insert (parent, elm, ref) {
if (parent) {
if (ref) {
if (ref.parentNode === parent) {
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref);
}
} else {
nodeOps.appendChild(parent, elm)
}
}
}createElm
createElm 用来新建一个节点, tag 存在创建一个标签节点,否则创建一个文本节点。
function createElm (vnode, parentElm, refElm) {
if (vnode.tag) {
insert(parentElm, nodeOps.createElement(vnode.tag), refElm);
} else {
insert(parentElm, nodeOps.createTextNode(vnode.text), refElm);
}
}addVnodes
addVnodes 用来批量调用 createElm 新建节点。
function addVnodes (parentElm, refElm, vnodes, startIdx, endIdx) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
createElm(vnodes[startIdx], parentElm, refElm);
}
}removeNode
removeNode 用来移除一个节点。
function removeNode (el) {
const parent = nodeOps.parentNode(el);
if (parent) {
nodeOps.removeChild(parent, el);
}
}removeVnodes
removeVnodes 会批量调用 removeNode 移除节点。
function removeVnodes (parentElm, vnodes, startIdx, endIdx) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
const ch = vnodes[startIdx]
if (ch) {
removeNode(ch.elm);
}
}
}patch
diff 算法
patch 的核心就是 diff 算法,通过 diff 算法可以对比出两棵树的「差异」
假设我们现在有如下两颗树,它们分别是新老 VNode 节点,这时候到了 patch 的过程,我们需要将他们进行比对。 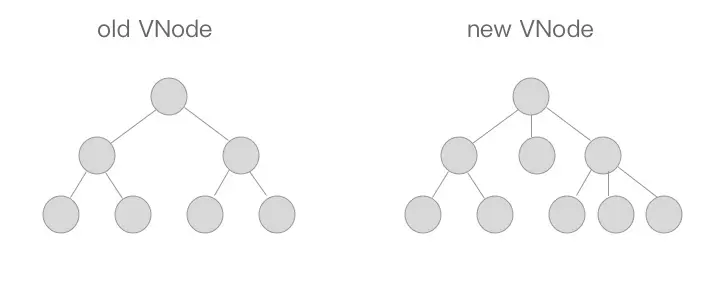
diff 算法是通过 同层的树节点进行比较,而非对树进行逐层搜索遍历的方式,所以时间复杂度只有O(n),是一种非常高效的算法。 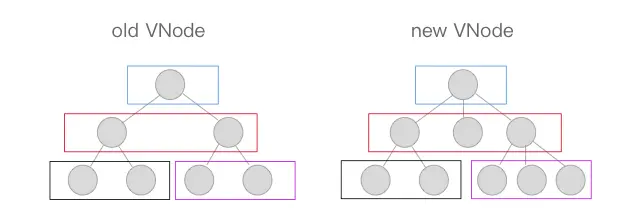
上图中相同颜色的方块中的节点会进行比对,比对得到「差异」后将这些「差异」更新到视图上。因为只进行同层级的比对,所以十分高效。
patch 过程简单代码:
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, parentElm) {
if (!oldVnode) {
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
} else if (!vnode) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
} else {
if (sameVnode(oldVNode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVNode, vnode);
} else {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
}
}
}因为 patch 的主要功能是比对两个 VNode 节点,将「差异」更新到视图上,所以入参有新老两个 VNode 以及父节点的 element 。
首先在 oldVnode(老 VNode 节点)不存在的时候,相当于新的 VNode 替代原本没有的节点,所以直接用 addVnodes 将这些节点批量添加到 parentElm 上。
if (!oldVnode) {
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
}然后同理,在 vnode(新 VNode 节点)不存在的时候,相当于要把老的节点删除,所以直接使用 removeVnodes 进行批量的节点删除即可。
else if (!vnode) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
}最后一种情况,当 oldVNode 与 vnode 都存在的时候,需要判断它们是否属于 sameVnode(相同的节点)。如果是则进行 patchVnode(比对 VNode )操作,否则删除老节点,增加新节点。
if (sameVnode(oldVNode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVNode, vnode);
} else {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
}sameVnode
什么情况下两个 VNode 会属于 sameVnode (相同的节点):
function sameVnode () {
return (
a.key === b.key &&
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
(!!a.data) === (!!b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
)
}
function sameInputType (a, b) {
if (a.tag !== 'input') return true
let i
const typeA = (i = a.data) && (i = i.attrs) && i.type
const typeB = (i = b.data) && (i = i.attrs) && i.type
return typeA === typeB
}sameVnode 其实很简单,只有当 key、 tag、 isComment(是否为注释节点)、 data同时定义(或不定义),同时满足当标签类型为 input 的时候 type 相同(某些浏览器不支持动态修改<input>类型,所以他们被视为不同类型)即可。
patchVnode
当新老VNode节点符合 sameVnode 条件,就会进行「比对」。
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return;
}
if (vnode.isStatic && oldVnode.isStatic && vnode.key === oldVnode.key) {
vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance;
return;
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
const oldCh = oldVnode.children;
const ch = vnode.children;
if (vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text);
} else {
if (oldCh && ch && (oldCh !== ch)) {
updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch);
} else if (ch) {
if (oldVnode.text) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '');
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1);
} else if (oldCh) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (oldVnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
}
}首先在新老Vnode节点相同的情况下,就不需要做任何改变了,直接 return 掉
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return;
}在当新老 VNode 节点都是 isStatic(静态的),并且 key 相同时,只要将 componentInstance 与 elm 从老 VNode 节点“拿过来”即可。这里的 isStatic 也就是前面提到过的「编译」的时候会将静态节点标记出来,这样就可以跳过比对的过程。
if (vnode.isStatic && oldVnode.isStatic && vnode.key === oldVnode.key) {
vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance;
return;
}接下来,当新 VNode 节点是文本节点的时候,直接用 setTextContent 来设置 text,这里的 nodeOps 是一个适配层,根据不同平台提供不同的操作平台 DOM 的方法,实现跨平台。
if (vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text);
}当新 VNode 节点是非文本节点当时候,需要分几种情况:
oldCh与ch都存在且不相同时,使用updateChildren函数来更新子节点 (这个重点)- 如果只有
ch存在的时候,如果老节点是文本节点则先将节点的文本清除,然后将ch批量插入插入到节点elm下。 - 同理当只有
oldch存在时,说明需要将老节点通过removeVnodes全部清除。 - 最后一种情况是当只有老节点是文本节点的时候,清除其节点文本内容。
if (oldCh && ch && (oldCh !== ch)) {
updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch);
} else if (ch) {
if (oldVnode.text) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '');
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1);
} else if (oldCh) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (oldVnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}updateChildren
函数代码:
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh) {
let oldStartIdx = 0;
let newStartIdx = 0;
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1;
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1;
let newStartVnode = newCh[0];
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx];
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, elmToMove, refElm;
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (!oldStartVnode) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
} else if (!oldEndVnode) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode);
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm));
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode);
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
let elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (!oldKeyToIdx) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
idxInOld = newStartVnode.key ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key] : null;
if (!idxInOld) {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (sameVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode);
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined;
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, newStartVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = (newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm : null;
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx);
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
}首先定义 oldStartIdx、newStartIdx、oldEndIdx 以及 newEndIdx 分别是新老两个 VNode 的两边的索引,同时 oldStartVnode、newStartVnode、oldEndVnode 以及 newEndVnode 分别指向这几个索引对应的 VNode 节点。 
接下来是一个 while 循环,在这过程中,oldStartIdx、newStartIdx、oldEndIdx 以及 newEndIdx 会逐渐向中间靠拢。
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx)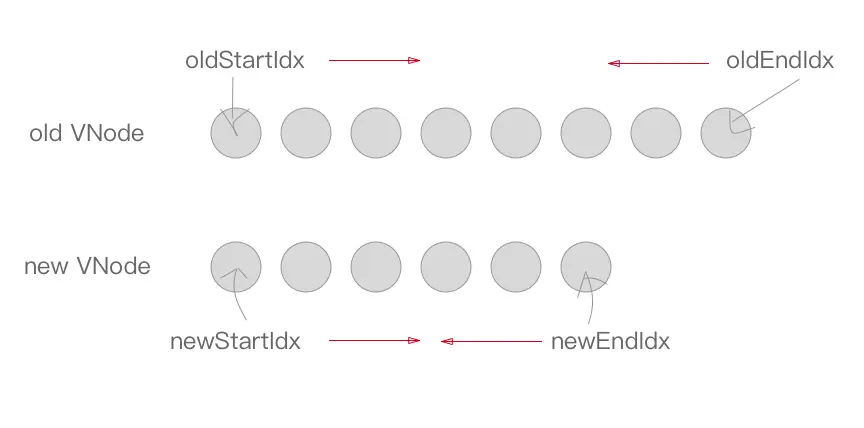
首先当 oldStartVnode 或者 oldEndVnode 不存在的时候,oldStartIdx 与 oldEndIdx 继续向中间靠拢,并更新对应的 oldStartVnode 与 oldEndVnode 的指向(注:下面的 oldStartIdx、newStartIdx、oldEndIdx 以及 newEndIdx 移动都会伴随着 oldStartVnode、newStartVnode、oldEndVnode 以及 newEndVnode 的指向的变化,之后的部分只会讲 Idx 的移动)。
if (!oldStartVnode) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
} else if (!oldEndVnode) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
}接下来这一块,是将 oldStartNode、newStartVnode、oldEndVnode 以及 newEndVnode 两两比对的过程,一共会出现 2*2=4 种情况。
else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode);
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm));
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode);
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}首先是 oldStartVnode 与 newStartVnode 符合 sameVnode 时,说明老 VNode 节点的头部与新 VNode 节点的头部是相同的 VNode 节点,直接进行 patchVnode,同时 oldStartIdx 与 newStartIdx 向后移动一位。 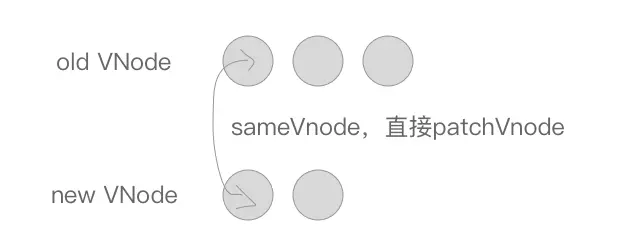
其次是 oldEndVnode 与 newEndVnode 符合 sameVnode ,也就是两个 VNode 的结尾是相同的 VNode,同样进行 patchVnode 操作并将 oldEndVnode 与 newEndVnode 向前移动一位。 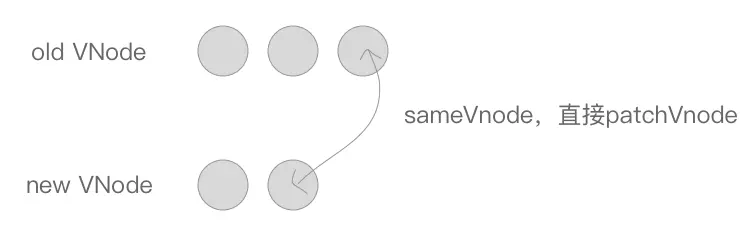
接下来是两种交叉的情况:
先是 oldStartVnode 与 newEndVnode 符合 sameVnode 的时候,也就是老 VNode 节点的头部与新 VNode 节点的尾部是同一节点的时候,将 oldStartVnode.elm 这个节点直接移动到 oldEndVnode.elm 这个节点的后面即可。然后 oldStartIdx 向后移动一位,newEndIdx 向前移动一位。 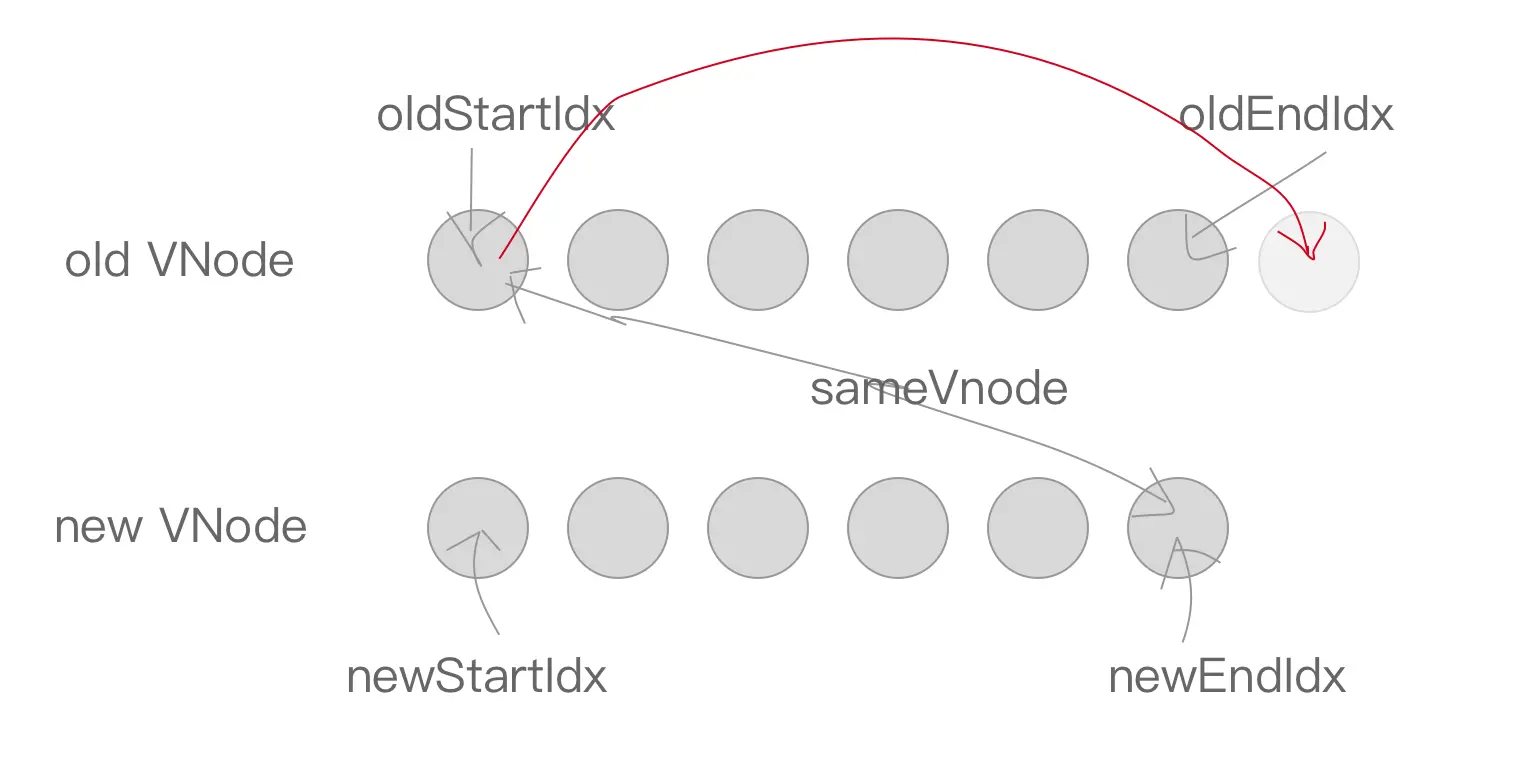
同理,oldEndVnode 与 newStartVnode 符合 sameVnode 时,也就是老 VNode 节点的尾部与新 VNode 节点的头部是同一节点的时候,将 oldEndVnode.elm 插入到 oldStartVnode.elm 前面。同样的,oldEndIdx 向前移动一位,newStartIdx 向后移动一位。 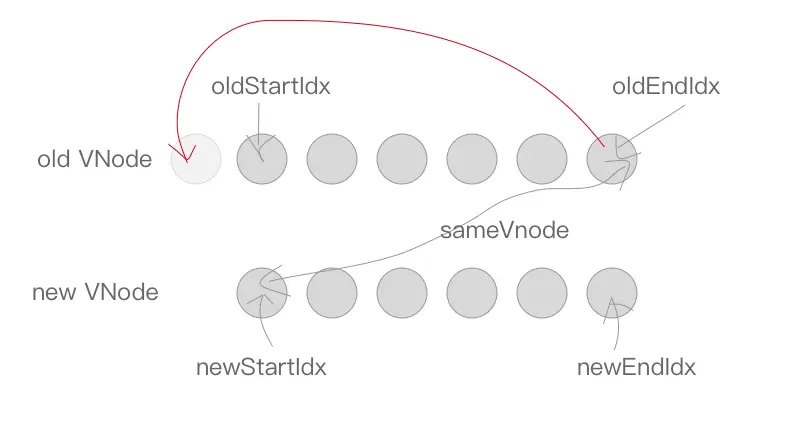
最后是当以上情况都不符合的时候,这种情况怎么处理呢?
else {
let elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (!oldKeyToIdx) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
idxInOld = newStartVnode.key ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key] : null;
if (!idxInOld) {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (sameVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode);
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined;
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, newStartVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
}
function createKeyToOldIdx (children, beginIdx, endIdx) {
let i, key
const map = {}
for (i = beginIdx; i <= endIdx; ++i) {
key = children[i].key
if (isDef(key)) map[key] = i
}
return map
}createKeyToOldIdx 的作用是产生 key 与 index 索引对应的一个 map 表。比如说:
[
{xx: xx, key: 'key0'},
{xx: xx, key: 'key1'},
{xx: xx, key: 'key2'}
]在经过 createKeyToOldIdx 转化以后会变成:
{
key0: 0,
key1: 1,
key2: 2
}我们可以根据某一个 key 的值,快速地从 oldKeyToIdx(createKeyToOldIdx 的返回值)中获取相同 key 的节点的索引 idxInOld,然后找到相同的节点。
如果没有找到相同的节点,则通过 createElm 创建一个新节点,并将 newStartIdx 向后移动一位。
if (!idxInOld) {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}否则如果找到了节点,同时它符合 sameVnode ,则将这两个节点进行 patchVnode ,将该位置的老节点赋值 undefined(之后如果还有新节点与该节点key相同可以检测出来提示已有重复的 key ),同时将 newStartVnode.elm 插入到 oldStartVnode.elm 的前面。同理,newStartIdx 往后移动一位。 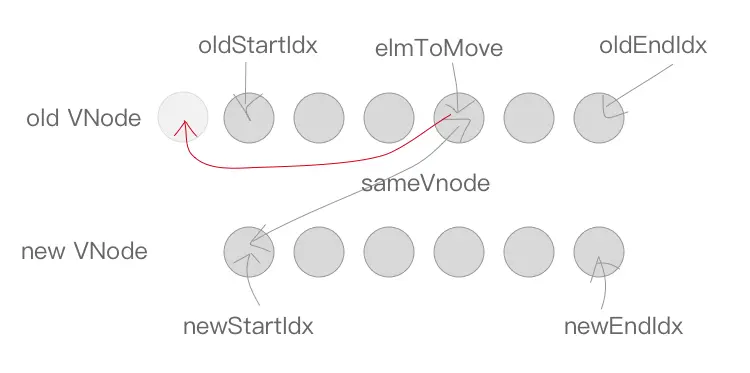
else {
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
if (sameVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode);
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined;
nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, newStartVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}如果不符合 sameVnode,只能创建一个新节点插入到 parentElm 的子节点中,newStartIdx 往后移动一位。 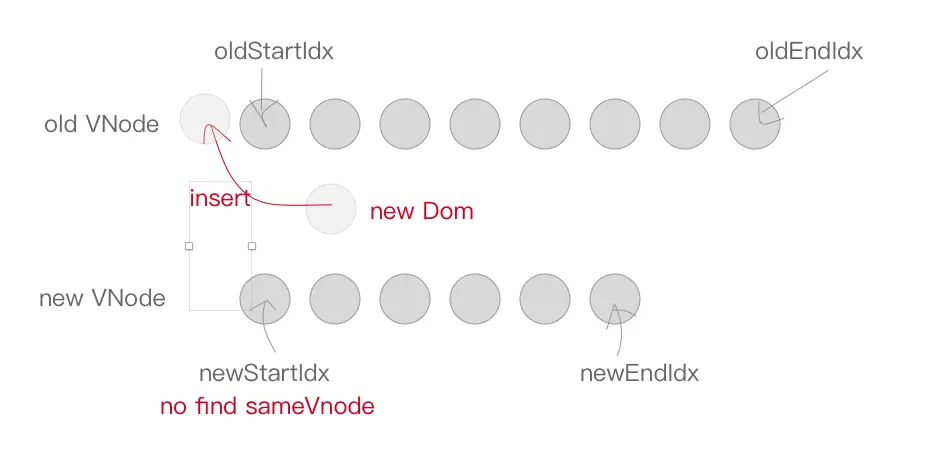
else {
createElm(newStartVnode, parentElm);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}最后一步就很容易啦,当 while 循环结束以后,如果 oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx,说明老节点比对完了,但是新节点还有多的,需要将新节点插入到真实 DOM 中去,调用 addVnodes 将这些节点插入即可。 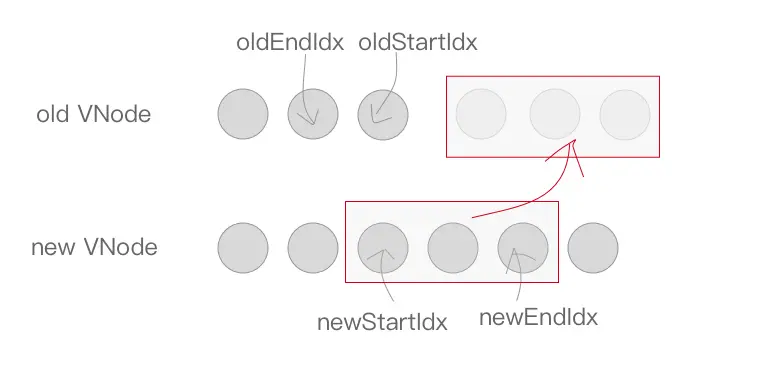
同理,如果满足 newStartIdx > newEndIdx 条件,说明新节点比对完了,老节点还有多,将这些无用的老节点通过 removeVnodes 批量删除即可。 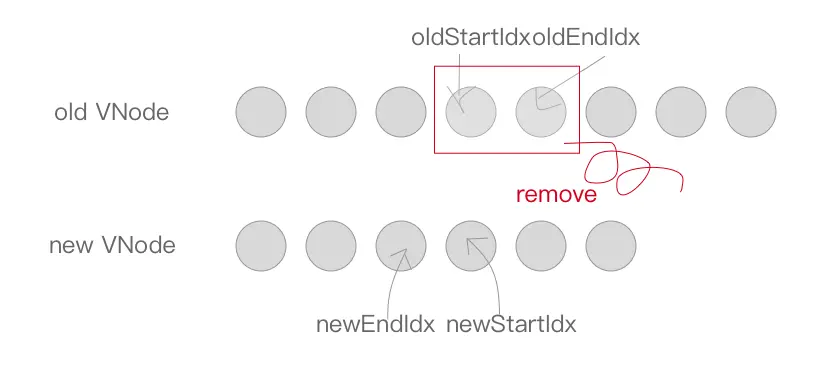
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = (newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm : null;
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx);
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}🎉🎉over!
本文为学习剖析 Vue.js 内部运行机制时的笔记
